

- #NUMBERS FOR MAC COPY FORMULAS TO OTHER COLUMNS FULL#
- #NUMBERS FOR MAC COPY FORMULAS TO OTHER COLUMNS PLUS#
This is where the Transpose function comes in.įirst, select a range of blank cells beneath (or on another sheet) that’s the same size as the original range.
Why would anyone do this? Sometimes when spreadsheets are created, we aren’t absolutely certain which data should be the fields and which should be the records and, sometimes, the situation changes and requires a redesign. =TRANSPOSEĪ very useful function if you decide to change the spreadsheet fields (columns) to rows and vice versa. =COUNTA(B13:B22) + COUNTBLANK(B13:B22) JD Sartain / IDGĬheckout the Average, FormulaText, and four Count functions 11. Note: Don’t forget to put the conditions inside double quotes, or else you’ll receive an error. First you count the cells, then set the condition for example: =COUNTIF(C13:C22, “<19”).
This formula combines the COUNT and the IF functions to count the number of cells in a range that meet a specific condition.įor example, say that you want to count the number of members in the Music Club (column C), but only the members who receive the discounted price of $18.00 a month. In other words, if you put a space in cell B13, the total blank cells changes from 4 to 3. Note that anything in a cell, even a space, will register as a non-blank cell. In column B of our spreadsheet example, there are four blank cells (and six cells with numbers). The COUNTBLANK function does exactly what is says: It counts the number of blank cells in a column or range. For example =COUNT(B12:B21) tells us there are six people in the Garden Club.
#NUMBERS FOR MAC COPY FORMULAS TO OTHER COLUMNS FULL#
Use the COUNT function to total the number of people in each club (without having to create a column full of ones). The spreadsheet adds the dues for all clubs in column G, so each individual knows how much he/she owes in dues a month. Why use the COUNT function? Imagine that your friends pay dues for membership into several different clubs.
#NUMBERS FOR MAC COPY FORMULAS TO OTHER COLUMNS PLUS#
COUNT only counts numbers and formulas, while COUNTA counts everything-that is, alpha and numeric characters plus punctuation, symbols, and even spaces.

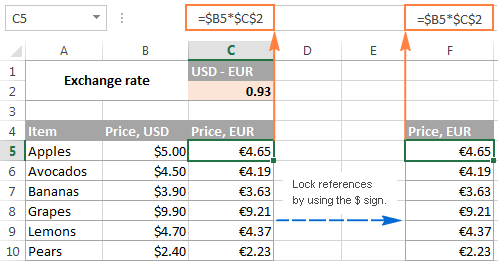
These simple functions count the total number of digits or text in a column of data. So typing =AVERAGE(E2:E6) adds those five numbers, then divides by 6. Before functions, to get an average, you would add a column of numbers for example 10 numbers then divide by that total (10). =AVERAGEĪverages are used every day to determine the median or midpoint of a set of numbers for example, average grades for a group of students average temperature of a region and/or average height of sixth graders. So enter this formula into a cell off to the side of your spreadsheet matrix (such as cell F2): =FORMULATEXT(E2) and Excel displays the actual formula of E2. Sometimes it’s helpful, even necessary, to see the actual function, especially if you’re editing a macro or tracking down a circular reference. For example, the actual formula in cell E2 is =SUM(C2*D2) but all you see is the answer, which is $164.25. Use this function to display the “text” of a formula in a given cell. This is a handy formula to calculate the number of days between two dates (so there’s no worries about how many days are in each month of the range).Įxample: End Date Octominus Start Date Ma= 195 days Repeat this process for formulas that calculate a range of cells (e.g., beginning date, ending date, etc.) 1. Pointing means you click the field box first, then click the corresponding cell over in the worksheet. When Excel displays the various cell/range dialog boxes, you can either manually enter the cell/range address, or cursor and point to it. Note: Some formulas require you to input the single cell or range address of the values or text you want calculated. The five formulas below may have somewhat inscrutable names, but their functions save time and data entry on a daily basis. – Excel: Scenario Planning and Analysis 12 handy formulas for common tasks Here are our top picks to start with:Ĭoursera – Excel Skills for Business: EssentialsĮDX – Analyzing and Visualizing Data with Excel If you want to deepen your Excel mastery, a number of online courses exist to expand your knowledge.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
